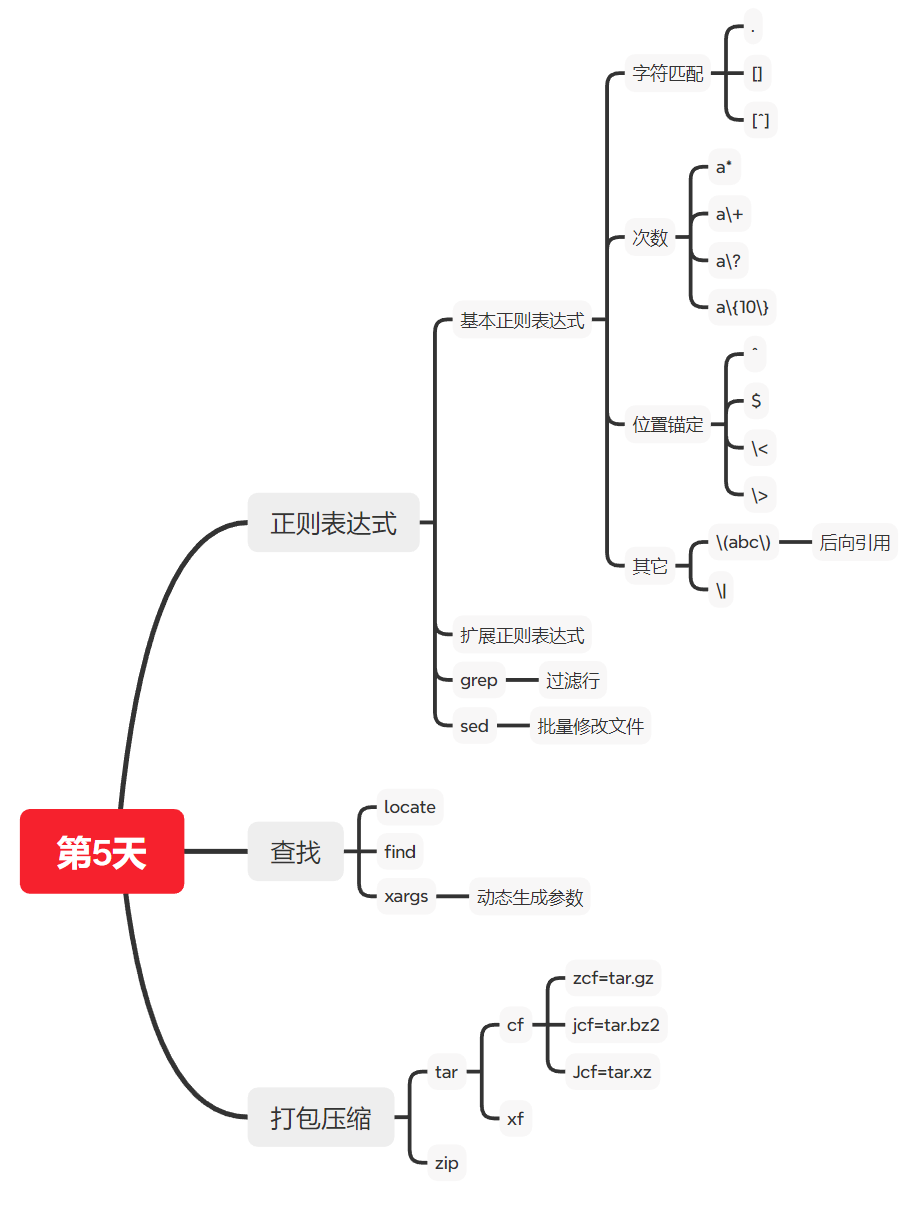
文本处理三剑客
文本处理三剑客
grep 命令主要对文本的(正则表达式)行基于模式进行过滤
sed:stream editor,文本编辑工具
awk:Linux上的实现gawk,文本报告生成器
文本处理三剑客之 grep
grep: Global search REgular expression and Print out the line
作用:文本搜索工具,根据用户指定的“模式”对目标文本逐行进行匹配检查;打印匹配到的行
模式:由正则表达式字符及文本字符所编写的过滤条件
帮助
https://man7.org/linux/man-pages/man1/grep.1.html
格式:
grep [OPTIONS] PATTERN [FILE...]
常见选项:
--color:将匹配的文本高亮显示。
-m # 匹配#次后停止
-i:忽略大小写。例如,grep -i "pattern" file.txt 将匹配 “pattern”、“Pattern”、“PATTERN” 等。
-v:反转匹配,只显示不匹配指定模式的行。例如,grep -v "pattern" file.txt 将显示不包含 “pattern” 的所有行。
-c:计数,只输出匹配行的数量,不显示匹配的内容。例如,grep -c "pattern" file.txt 将输出匹配 “pattern” 的行数。
-q 静默模式,不输出任何信息
-n:显示匹配行及其行号。例如,grep -n "pattern" file.txt 将输出匹配 “pattern” 的行及其在文件中的行号。
-r 或 -R:递归搜索,但不处理软链接。在目录中递归地搜索包含指定模式的文件。例如,grep -r "pattern" /path/to/directory/。
-R 递归目录,但处理软链接
-l:只输出包含匹配字符串的文件名,不输出匹配行的内容。例如,grep -l "pattern" *.txt。
-L:与 -l 相反,只输出不包含匹配字符串的文件名。
-E:使用扩展正则表达式。例如,grep -E "pattern1|pattern2" file.txt 将匹配包含 “pattern1” 或 “pattern2” 的行。
-o:只输出匹配到的部分,而不是整行内容。
-A [num]:打印匹配行及其后的 [num] 行。例如,grep -A 2 "pattern" file.txt 将输出匹配 “pattern” 的行及其后的两行。
-B [num]:打印匹配行及其前的 [num] 行。
-C [num] 或 --context=[num]:打印匹配行及其前后的 [num] 行。
-w 匹配整个单词
-e:指定多个搜索模式。例如,grep -e "pattern1" -e "pattern2" file.txt。
-f:从文件中读取搜索模式。例如,grep -f patterns.txt file.txt。
-F 不支持正则表达式,相当于fgrep
-P 支持Perl格式的正则表达式
这些选项可以组合使用,以实现更复杂的搜索和过滤任务。例如,grep -i -r -n “pattern” /path/to/directory/ 将递归地在指定目录中搜索包含 “pattern” 的所有文件,忽略大小写,并显示匹配行的行号。 范例:
grep root /etc/passwd
grep "USER" /etc/passwd
grep 'USER' /etc/passwd
grep whoami /etc/passwd
范例:
[root@ubuntu2004 ~]#grep -c processor /proc/cpuinfo
2
范例:取两个文件的相同行
[root@centos8 ~]#cat /data/f1.txt
a
b
1
c
[root@centos8 ~]#cat /data/f2.txt
b
e
f
c
1
2
[root@centos8 ~]#grep -f /data/f1.txt /data/f2.txt
b
c
1
[root@centos8 ~]#cat /data/f1.txt /data/f2.txt| sort | uniq -d
范例: 分区利用率最大的值
[root@centos8 ~]#df | grep '^/dev/sd' |tr -s ' ' %|cut -d% -f5|sort -n|tail -1
[root@centos8 ~]#df |grep '^/dev/sd' |grep -oE '\<[0-9]{,3}%'|tr -d '%'|sort -
nr|head -n1
[root@centos8 ~]#df |grep '^/dev/sd' |grep -oE '\<[0-9]{,3}%'|grep -Eo '[0-9]+'
|sort -nr|head -n1
13
范例: 哪个IP和当前主机连接数最多的前三位
[root@centos8 ~]#ss -nt | grep "^ESTAB" |tr -s ' ' : |cut -d: -f6|sort |uniq -
c|sort -nr|head -n3
3 10.0.0.1
1 172.16.4.100
1 172.16.31.188
范例: 连接状态的统计
[root@wang-liyun-pc ~]# ss -nta | grep -v '^State' |cut -d" " -f1|sort |uniq -c
7 ESTAB
4 LISTEN
7 TIME-WAIT
[root@wang-liyun-pc ~]# ss -nta | tail -n +2 |cut -d" " -f1|sort |uniq -c
3 ESTAB
4 LISTEN
12 TIME-WAIT
范例:
[root@centos8 ~]#grep -v "^#" /etc/profile | grep -v '^$'
[root@centos8 ~]#grep -v "^#\|^$" /etc/profile
[root@centos8 ~]#grep -v "^\(#\|$\)" /etc/profile
[root@centos8 ~]#grep -Ev "^(#|$)" /etc/profile
[root@centos8 ~]#egrep -v "^(#|$)" /etc/profile
[root@centos6 ~]#egrep -v '^(#|$)' /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
范例:
[root@centos8 ~]#grep -o 'r..t' /etc/passwd
root
root
root
root
r/ft
rypt
范例:
[root@centos8 ~]#ifconfig | grep -E '[0-9]{1,3}.[0-9]{1,3}.[0-9]{1,3}.[0-9]
{1,3}'
inet 10.0.0.8 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 10.0.0.255
inet 172.16.0.123 netmask 255.255.0.0 broadcast 172.16.255.255
inet6 fe80::c11e:4792:7e77:12a4 prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x20<link>
inet 127.0.0.1 netmask 255.0.0.0
[root@centos8 ~]#ifconfig | grep -E '([0-9]{1,3}.){3}[0-9]{1,3}'
inet 10.0.0.8 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 10.0.0.255
inet 172.16.0.123 netmask 255.255.0.0 broadcast 172.16.255.255
inet6 fe80::c11e:4792:7e77:12a4 prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x20<link>
inet 127.0.0.1 netmask 255.0.0.0
[root@centos8 ~]#ifconfig eth0 | grep -Eo '([0-9]{1,3}\.){3}[0-9]{1,3}'|head -1
10.0.0.8
[root@centos8 ~]#cat regex.txt
([0-9]{1,3}\.){3}[0-9]{1,3}
[root@centos8 ~]#ifconfig | grep -oEf regex.txt
10.0.0.8
255.255.255.0
10.0.0.255
127.0.0.1
255.0.0.0
范例:
[root@centos8 ~]#grep -E 'root|bash' /etc/passwd
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
operator:x:11:0:operator:/root:/sbin/nologin
wang:x:1000:1000:wang:/home/wang:/bin/bash
mage:x:1001:1001::/home/mage:/bin/bash
xiaoming:x:1002:1002::/home/xiaoming:/bin/bash
roob:x:1003:1003::/home/roob:/bin/bash
[root@centos8 ~]#grep -e 'root' -e 'bash' /etc/passwd
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
operator:x:11:0:operator:/root:/sbin/nologin
wang:x:1000:1000:wang:/home/wang:/bin/bash
mage:x:1001:1001::/home/mage:/bin/bash
xiaoming:x:1002:1002::/home/xiaoming:/b
范例:
[root@centos8 ~]#grep -w root /etc/passwd
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
operator:x:11:0:operator:/root:/sbin/nologin
[root@centos8 ~]#grep '\<root\>' /etc/passwd
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
operator:x:11:0:operator:/root:/sbin/nologin
范例:
[root@centos8 ~]#grep "^\(.*\)\>.*\<\1$" /etc/passwd
sync:x:5:0:sync:/sbin:/bin/sync
shutdown:x:6:0:shutdown:/sbin:/sbin/shutdown
halt:x:7:0:halt:/sbin:/sbin/halt
bash:x:1008:1008::/home/bash:/bin/bash
nologin:x:1011:1011::/home/nologin:/sbin/nologin
[root@centos8 ~]#grep -E "^(.*)\>.*\<\1$" /etc/passwd
sync:x:5:0:sync:/sbin:/bin/sync
shutdown:x:6:0:shutdown:/sbin:/sbin/shutdown
halt:x:7:0:halt:/sbin:/sbin/halt
bash:x:1008:1008::/home/bash:/bin/bash
nologin:x:1011:1011::/home/nologin:/sbin/nologin
[root@centos8 ~]#egrep "^(.*)\>.*\<\1$" /etc/passwd
sync:x:5:0:sync:/sbin:/bin/sync
shutdown:x:6:0:shutdown:/sbin:/sbin/shutdown
halt:x:7:0:halt:/sbin:/sbin/halt
bash:x:1008:1008::/home/bash:/bin/bash
nologin:x:1011:1011::/home/nologin:/sbin/nologin
范例: 过滤掉文件的注释(包括#号的行)和空行
[root@centos8 ~]#grep -Ev '^$|#' /etc/fstab
UUID=01f1068e-6937-4fb2-b64b-0d7d6b85ad08 / xfs
defaults 0 0
UUID=cb21e5ce-edf6-4ed1-8df9-ba98520a68dc /boot xfs
defaults 0 0
UUID=9ea3524a-7cff-49a0-951e-8429a30bd0a0 /data xfs
defaults 0 0
UUID=42174d44-41aa-448b-88bc-fd36d6a49e39 swap swap
defaults 0 0
范例:面试题,算出所有人的年龄总和
[root@centos8 ~]#cat /data/age.txt
xiaoming=20
xiaohong=18
xiaoqiang=22
[root@centos8 ~]#cut -d"=" -f2 /data/age.txt|tr '\n' + | grep -Eo ".*[0-9]"|bc
60
[root@centos8 ~]#grep -Eo "[0-9]+" /data/age.txt | tr '\n' + | grep -Eo ".*[0-
9]"|bc
60
[root@centos8 ~]#grep -oE '[0-9]+' /data/age.txt| paste -s -d+|bc
60
文本处理三剑客之 sed
Sed是从文件或管道中读取一行,处理一行,输出一行;再读取一行,再处理一行,再输出一行,直到 最后一行。每当处理一行时,把当前处理的行存储在临时缓冲区中,称为模式空间(Pattern Space),接着用sed命令处理缓冲区中的内容,处理完成后,把缓冲区的内容送往屏幕。接着处理下 一行,这样不断重复,直到文件末尾。一次处理一行的设计模式使得sed性能很高,sed在读取大文件时 不会出现卡顿的现象。如果使用vi命令打开几十M上百M的文件,明显会出现有卡顿的现象,这是因为 vi命令打开文件是一次性将文件加载到内存,然后再打开。Sed就避免了这种情况,一行一行的处理, 打开速度非常快,执行速度也很快。
助参考网站: http://www.gnu.org/software/sed/manual/sed.htm
sed 基本用法
sed [option]... 'script;script;...' [inputfile...]
常用选项:
-n 不输出模式空间内容到屏幕,即不自动打印
-e 多点编辑
-f FILE 从指定文件中读取编辑脚本
-r, -E 使用扩展正则表达式
-i.bak 备份文件并原处编辑
-s 将多个文件视为独立文件,而不是单个连续的长文件流
#说明:
-ir 不支持
-i -r 支持
-ri 支持
-ni 危险选项,会清空文件
script 格式:
'地址命令'
地址格式:
1. 不给地址:对全文进行处理
2. 单地址:
# 指定的行,$ 最后一行
/pattern/:被此处模式所能够匹配到的每一行
3. 地址范围:
#,# #从#行到第#行,3,6 从第3行到第6行
#,+# #从#行到+#行,3,+4 表示从3行到第7行
/pat1/,/pat2/
#,/pat/
/pat/,#
4. 步进:~
1~2 奇数行
2~2 偶数行
命令:
p 打印当前模式空间内容,追加到默认输出之后
Ip 忽略大小写输出
d 删除模式空间匹配的行,并立即启用下一轮循环
a [\]text 在指定行后面追加文本,支持使用\n实现多行追加
i [\]text 在行前面插入文本
c [\]text 替换行为单行或多行文本
w file 保存模式匹配的行至指定文件
r file 读取指定文件的文本至模式空间中匹配到的行后
= 为模式空间中的行打印行号
! 模式空间中匹配行取反处理
q 结束或退出sed
查找替代
s/pattern/string/修饰符 查找替换,支持使用其它分隔符,可以是其它形式:s@@@,s###
替换修饰符:
g 行内全局替换
p 显示替换成功的行
w /PATH/FILE 将替换成功的行保存至文件中
I,i 忽略大小写
范例:
#默认sed会将输入信息直接输出
[root@centos8 ~]#sed ''
welcome
welcome
to
to
magedu
magedu
[root@centos8 ~]#sed '' /etc/issue
\S
Kernel \r on an \m
[root@centos8 ~]#sed 'p' /etc/issue
\S
\S
Kernel \r on an \m
Kernel \r on an \m
[root@centos8 ~]#sed -n '' /etc/issue
[root@centos8 ~]#sed -n 'p' /etc/issue
\S
Kernel \r on an \m
[root@centos8 ~]#sed -n '1p' /etc/passwd
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
[root@centos8 ~]# ifconfig ens18 | sed '2p'
ens18: flags=4163<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST> mtu 1500
inet 192.168.5.170 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 192.168.5.255
inet 192.168.5.170 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 192.168.5.255
inet6 fe80::be24:11ff:fe18:d19a prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x20<link>
inet6 2409:8a50:c25:f510:be24:11ff:fe18:d19a prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x0<global>
ether bc:24:11:18:d1:9a txqueuelen 1000 (Ethernet)
RX packets 1378000 bytes 118404343 (112.9 MiB)
RX errors 0 dropped 6119 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 854304 bytes 98993817 (94.4 MiB)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
[root@centos8 ~]# ifconfig ens18 | sed -n '2p'
inet 192.168.5.170 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 192.168.5.255
[root@centos8 ~]#sed -n '$p' /etc/passwd
postfix:x:89:89::/var/spool/postfix:/sbin/nologin
#倒数第二行
[root@ubuntu1804 ~]#sed -n "$(echo $[`cat /etc/passwd|wc -l`-1])p" /etc/passwd
[root@centos8 ~]#ifconfig eth0 |sed -n '/netmask/p'
inet 10.0.0.8 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 10.0.0.255
[root@centos8 ~]#df | sed -n '/^\/dev\/sd/p'
/dev/sda2 104806400 4872956 99933444 5% /
/dev/sda3 52403200 398860 52004340 1% /data
/dev/sda1 999320 848568 81940 92% /boot
[root@centos8 ~]#seq 10 | sed -n '3,6p'
3
4
5
6
[root@centos8 ~]#seq 10 | sed -n '3,+4p'
3
4
5
6
7
[root@centos8 ~]#seq 10 | sed -n '3,$p'
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
[root@centos8 ~]#seq 10 |sed -n '1~2p'
1
3
5
7
9
[root@centos8 ~]#seq 10 |sed -n '2~2p'
2
4
6
8
10
[root@centos8 ~]#seq 10 |sed '1~2d'
2
4
6
8
10
[root@centos8 ~]#seq 10 |sed '2~2d'
1
3
5
7
9
[root@centos8 ~]#sed -e '2d' -e '4d' seq.log
1
3
5
6
7
8
9
10
[root@centos8 ~]#sed '2d;4d' seq.log
1
3
5
6
7
8
9
10
#不显示注释行和空行
[root@centos6 ~]#sed '/^#/d;/^$/d' /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
[root@centos6 ~]#grep -Ev '^#|^$' /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
[root@centos8 ~]#sed -i.orig '2d;4d' seq.log
[root@centos8 ~]#cat seq.log.orig
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
[root@centos8 ~]#cat seq.log
1
3
5
6
7
8
9
10
[root@centos8 ~]#seq 10 > seq.log
[root@centos8 ~]#sed -i.orig '2d;4d' seq.log
[root@centos8 ~]#sed -i '/^listen 9527/a listen 80 \nlisten 8080'
/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
#删除所有以#开头的行
[root@centos8 ~]#sed -i '/^#/d' fstab
#只显示非#开头的行
[root@centos8 ~]#sed -n '/^#/!p' fstab
#修改网卡配置
[root@centos8 ~]#sed -Ei.bak '/^GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX/s/(.*)(")$/\1
net.ifnames=0\2/' /etc/default/grub
范例: 搜索替换和&
[root@centos8 ~]#sed -nr 's/r..t/&er/gp' /etc/passwd
rooter:x:0:0:rooter:/rooter:/bin/bash
operator:x:11:0:operator:/rooter:/sbin/nologin
ftp:x:14:50:FTP User:/var/fterp:/sbin/nologin
范例: 除指定文件外其余删除
[root@rocky8 ~]#rm -f `ls | grep -Ev '(3|5|7)\.txt'`
[root@rocky8 ~]#ls | sed -n '/[^357].txt/p'|xargs rm
[root@rocky8 ~]#ls | grep -Ev '(3|5|7)\.txt' | sed -n 's/.*/rm &/p'|bash
[root@rocky8 ~]#ls | grep -Ev '(3|5|7)\.txt' | sed -En 's/(.*)/rm \1/p'|bash
范例: 获取分区利用率
[root@centos8 ~]#df | sed -En '/^\/dev\/sd/s@.* ([0-9]+)%.*@\1@p'
3
1
13
范例:
sed '2p' /etc/passwd
sed -n '2p' /etc/passwd
sed -n '1,4p' /etc/passwd
sed -n '/root/p' /etc/passwd
sed -n '2,/root/p' /etc/passwd 从2行开始
sed -n '/^$/=' file 显示空行行号
sed -n -e '/^$/p' -e '/^$/=' file
Sed'/root/a\superman' /etc/passwd行后
sed '/root/i\superman' /etc/passwd 行前
sed '/root/c\superman' /etc/passwd 代替行
sed '/^$/d' file
sed '1,10d' file
nl /etc/passwd | sed '2,5d'
nl /etc/passwd | sed '2a tea'
sed 's/test/mytest/g' example
sed -n 's/root/&superman/p' /etc/passwd 单词后
sed -n 's/root/superman&/p' /etc/passwd 单词前
sed -e 's/dog/cat/' -e 's/hi/lo/' pets
sed -i.bak 's/dog/cat/g' pets
范例:取IP 地址
[root@centos8 ~]#ifconfig eth0 |sed -nr "2s/[^0-9]+([0-9.]+).*/\1/p"
10.0.0.8
[root@centos6 ~]#ifconfig eth0 | sed -En '2s/^[^0-9]+([0-9.]{7,15}).*/\1/p'
10.0.0.6
[root@centos8 ~]#ifconfig eth0 | sed -rn '2s/^[^0-9]+([0-9.]+) .*$/\1/p'
10.0.0.8
[root@centos8 ~]#ifconfig eth0 | sed -n '2s/^.*inet //p' | sed -n 's/
netmask.*//p'
10.0.0.8
[root@centos8 ~]#ifconfig eth0 | sed -n '2s/^.*inet //;s/ netmask.*//p'
10.0.0.8
[root@centos8 ~]#ifconfig eth0 | sed -rn '2s/(.*inet )([0-9].*)(
netmask.*)/\2/p'
10.0.0.8
范例:取基名和目录名
echo "/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/" |sed -r 's#(^/.*/)([^/]+/?)#\2#' 取基名
echo "/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/" |sed -r 's#(^/.*/)([^/]+/?)#\1#' 取目录
#取目录名
[root@centos8 ~]#echo /etc/sysconfig/ | sed -rn 's#(.*)/([^/]+)/?#\1#p'
/etc
#取基名
[root@centos8 ~]#echo /etc/sysconfig/ | sed -rn 's#(.*)/([^/]+)/?#\2#p'
sysconfig
范例: 取文件的前缀和后缀
[root@centos8 data]#echo a.b.c.gz |sed -En 's/(.*)\.([^.]+)$/\1/p'
a.b.c
[root@centos8 data]#echo a.b.c.gz |sed -En 's/(.*)\.([^.]+)$/\2/p'
gz
[root@centos8 data]#echo a.b.c.gz |grep -Eo '.*\.'
a.b.c
[root@centos8 data]#echo a.b.c.gz |grep -Eo '[^.]+$'
gz
[root@centos8 ~]#echo a.b.tar.gz | sed -rn 's@.*\.([^.]+)\.([^.]+)$@\1.\2@p'
tar.gz
范例:将非#开头的行加#
[root@centos8 ~]#sed -rn "s/^[^#]/#&/p" /etc/fstab
#UUID=1b950ef9-7142-46bd-975c-c4ac1e0d47e8 / xfs
defaults 0 0
#UUID=667a4c81-8b4b-4a39-a111-b11cb6d09309 /boot ext4
defaults 1 2
#UUID=38d14714-c018-41d5-922c-49e415decbca /data xfs
defaults 0 0
#UUID=a0efb2bb-8227-4317-a79d-0a70d515046c swap swap
defaults 0 0
[root@centos8 ~]#sed -rn 's/^[^#](.*)/#\1/p' /etc/fstab
#UID=1b950ef9-7142-46bd-975c-c4ac1e0d47e8 / xfs
defaults 0 0
#UID=667a4c81-8b4b-4a39-a111-b11cb6d09309 /boot ext4
defaults 1 2
#UID=38d14714-c018-41d5-922c-49e415decbca /data xfs
defaults 0 0
#UID=a0efb2bb-8227-4317-a79d-0a70d515046c swap swap
defaults 0 0
[root@centos8 ~]#sed -rn '/^#/!s@^@#@p' /etc/fstab
#
#UUID=1b950ef9-7142-46bd-975c-c4ac1e0d47e8 / xfs
defaults 0 0
#UUID=667a4c81-8b4b-4a39-a111-b11cb6d09309 /boot ext4
defaults 1 2
#UUID=38d14714-c018-41d5-922c-49e415decbca /data xfs
defaults 0 0
#UUID=a0efb2bb-8227-4317-a79d-0a70d515046c swap swap
defaults 0 0
范例:将#开头的行删除#
[root@centos8 ~]#sed -ri.bak '/^#/s/^#//' /etc/fstab
范例:取分区利用率
[root@centos8 ~]#df | sed -nr '/^\/dev\/sd/s# .* ([0-9]+)%.*# \1#p'
/dev/sda2 3
/dev/sda5 1
/dev/sda1 14
[root@centos8 ~]#df | sed -rn '/^\/dev\/sd/ s#([^[:space:]]+[[:space:]]+){4}
(.*)%.*#\2#p'
3
1
19
[root@centos8 ~]#df | sed -rn '/^\/dev\/sd/ s#(\S+\s+){4}(.*)%.*#\2#p'
3
1
19
范例:修改内核参数
[root@centos8 ~]#sed -nr '/^GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX/s/"$/ net.ifnames=0"/p'
/etc/default/grub
GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX="crashkernel=auto resume=UUID=8363289d-138e-4e4a-abaf-
6e028babc924 rhgb quiet net.ifnames=0"
[root@centos8 ~]#sed -rn '/^GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX=/s@(.*)"$@\1 net.ifnames=0"@p'
/etc/default/grub
GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX="crashkernel=auto resume=UUID=a0efb2bb-8227-4317-a79d-
0a70d515046c rhgb quiet net.ifnames=0"
[root@centos8 ~]#sed -rn '/^GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX=/s@"$@ net.ifnames=0"@p'
/etc/default/grub
GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX="crashkernel=auto resume=UUID=a0efb2bb-8227-4317-a79d-
0a70d515046c rhgb quiet net.ifnames=0 net.ifnames=0"
范例:修改网卡名称
#centos7,8
[root@centos8 ~]#sed -i '/GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX=/s#quiet#& net.ifnames=0#'
/etc/default/grub
[root@centos8 ~]#sed -ri '/^GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX=/s@"$@ net.ifnames=0"@'
/etc/default/grub
[root@centos8 ~]#grub2-mkconfig -o /boot/grub2/grub.cfg
#ubuntu
[root@ubuntu ~]#grub-mkconfig -o /boot/grub/grub.cfg
范例:查看配置文件
#过滤掉空行和#开头的行
sed -r '/^(#|$)/d' /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
sed -r '/^#|^$/d' /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
#可以排除行首后加多个空白符之后有#这种行
sed -n '/^$/d;/^[[:space:]]*#/!p' /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
sed -n -e '/^$/d' -e '/^[[:space:]]*#/!p' /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
#注意:以下前后顺序不同,执行效果不同
sed -n '/^[[:space:]]*#/!p;/^$/d' /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
sed -n -e '/^[[:space:]]*#/!p' -e '/^$/d' /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
范例:引用变量
[root@centos8 ~]#echo|sed "s/^/$RANDOM.rmvb/"
5242.rmvb
[root@centos8 ~]#echo|sed 's/^/$RANDOM.rmvb/'
$RANDOM.rmvb
[root@centos8 ~]#echo|sed 's/^/'$RANDOM'.rmvb/'
13849.rmvb
[root@centos8 ~]#echo|sed 's/^/'''$RANDOM'''.rmvb/'
28767.rmvb
范例:修改配置文件
[root@centos6 ~]#sed -e '/^#<VirtualHost/,/^#<\/VirtualHost>/s@#@@' -e
'/^#NameVirtualHost/s@#@@' /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
范例: 变量实现多点编辑配置文件
[root@centos8 ~]#port=8080
[root@centos8 ~]#sed -ri.bak -e 's/^Listen 80/Listen '$port'/' -e "/ServerName/c
ServerName `hostname`:$port" /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
范例: 显示前10行
[root@centos8 ~]#seq 100 > test.txt
[root@centos8 ~]#sed 10q test.txt
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
sed 高级用法
sed 中除了模式空间,还另外还支持保持空间(Hold Space),利用此空间,可以将模式空间中的数
据,临时保存至保持空间,从而后续接着处理,实现更为强大的功能。
常见的高级命令
P 打印模式空间开端至\n内容,并追加到默认输出之前
h 把模式空间中的内容覆盖至保持空间中
H 把模式空间中的内容追加至保持空间中
g 从保持空间取出数据覆盖至模式空间
G 从保持空间取出内容追加至模式空间
x 把模式空间中的内容与保持空间中的内容进行互换
n 读取匹配到的行的下一行覆盖至模式空间
N 读取匹配到的行的下一行追加至模式空间
d 删除模式空间中的行
D 如果模式空间包含换行符,则删除直到第一个换行符的模式空间中的文本,并不会读取新的输入行,而使
用合成的模式空间重新启动循环。如果模式空间不包含换行符,则会像发出d命令那样启动正常的新循环
范例:
sed -n 'n;p' FILE
seq 10 | sed 'N;s/\n//'
sed '1!G;h;$!d' FILE
seq 10 | sed -n '/3/{g;1!p;};h' #前一行
seq 10 | sed -nr '/3/{n;p}' #后一行
sed 'N;D'FILE
seq 10 |sed '3h;9G;9!d'
sed '$!N;$!D' FILE
sed '$!d' FILE
sed 'G' FILE
sed 'g' FILE
sed '/^$/d;G' FILE
sed 'n;d' FILE
sed -n '1!G;h;$p' FIL
范例: 打印偶数行
[root@centos8 ~]#seq 10 | sed -n 'n;p'
2
4
6
8
10
[root@centos8 ~]#seq 10 | sed -n '2~2p'
2
4
6
8
10
[root@centos8 ~]#seq 10 | sed '1~2d'
2
4
6
8
10
[root@centos8 ~]#seq 10 | sed -n '1~2!p'
2
4
6
8
1
练习
1、删除centos7系统/etc/grub2.cfg文件中所有以空白开头的行行首的空白字符
2、删除/etc/fstab文件中所有以#开头,后面至少跟一个空白字符的行的行首的#和空白字符
3、在centos6系统/root/install.log每一行行首增加#号
4、在/etc/fstab文件中不以#开头的行的行首增加#号
5、处理/etc/fstab路径,使用sed命令取出其目录名和基名
6、利用sed 取出ifconfig命令中本机的IPv4地址
7、统计centos安装光盘中Package目录下的所有rpm文件的以.分隔倒数第二个字段的重复次数
8、统计/etc/init.d/functions文件中每个单词的出现次数,并排序(用grep和sed两种方法分别实现)
9、将文本文件的n和n+1行合并为一行,n为奇数行
文本处理三剑客之 awk
awk:Aho, Weinberger, Kernighan,报告生成器,格式化文本输出,GNU/Linux发布的AWK目前由自 由软件基金会(FSF)进行开发和维护,通常也称它为 GNU AWK